
Show Summary
John Hightower of Arch+Tower joined this edition of “Business Beat” to discuss the interplay of customer experience, employee experience, and operational excellence. Roger Lusby, CPA is the host of “Business Beat” and the series is presented by Alpharetta CPA firm Frazier & Deeter.
John Hightower, Arch + Tower

John Hightower is the CEO of Arch + Tower. Arch + Tower, an FD Company, helps their clients win in the Experience Economy. We are helping close the experience gaps for clients’ – Customers and Employees – delivered with Operational Excellence. They call it their CX/Ex/Ox Framework(tm).
They work with business leaders by creating solutions that help clients bridge gaps, stand up under the weight of growth, and build for the future, hence the name Arch + Tower.
Their team partners with clients to deploy proven methodologies and a comprehensive approach – technology, data, people, processes – to deliver excellence within an organization.
Arch + Tower has served companies like Chick-fil-A, ChenMed, Peak Campus, Sunstate Equipment, Thrive Farmers, and others planning to scale solutions across multiple locations.
Arch + Tower has joined the Frazier & Deeter family of companies. They are excited to be helping to improve customer and employee experiences as part of an award-winning accounting and advisory firm with offices across the US and the UK.
Visit www.archandtower.com to discover the ways their team can help you span gaps and see farther with your people and projects.
Frazier & Deeter
The Alpharetta office of Frazier & Deeter is home to a thriving CPA tax practice, a growing advisory practice and an Employee Benefit Plan Services group. CPAs and advisors in the Frazier & Deeter Alpharetta office serve clients across North Georgia and around the country with services such as personal tax planning, estate planning, business tax planning, business tax compliance, state and local tax planning, financial statement reviews, financial statement audits, employee benefit plan audits, internal audit outsourcing, cyber security, data privacy, SOX and other regulatory compliance, mergers and acquisitions and more. Alpharetta CPAs serve clients ranging from business owners and executives to large corporations.

Roger Lusby, host of Frazier & Deeter’s “Business Beat,” is an Alpharetta CPA and Alpharetta Office Managing Partner for Frazier & Deeter. He is also a member of the Tax Department in charge of coordinating tax and accounting services for our clientele. His responsibilities include a review of a variety of tax returns with an emphasis in the individual, estate, and corporate areas. Client assistance is also provided in the areas of financial planning, executive compensation and stock option planning, estate and succession planning, international planning (FBAR, SFOP), health care, real estate, manufacturing, technology and service companies.
You can find Frazier & Deeter on social media:
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/frazier-&-deeter-llc/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FrazierDeeter
Twitter: https://twitter.com/frazierdeeter
An episode archive of Frazier & Deeter’s “Business Beat” can be found here.










 With over 30 years’ experience,
With over 30 years’ experience, 



 “Decision Vision” is a podcast covering topics and issues facing small business owners and connecting them with solutions from leading experts. This series is presented by Brady Ware & Company. If you are a decision maker for a small business, we’d love to hear from you. Contact us at
“Decision Vision” is a podcast covering topics and issues facing small business owners and connecting them with solutions from leading experts. This series is presented by Brady Ware & Company. If you are a decision maker for a small business, we’d love to hear from you. Contact us at 


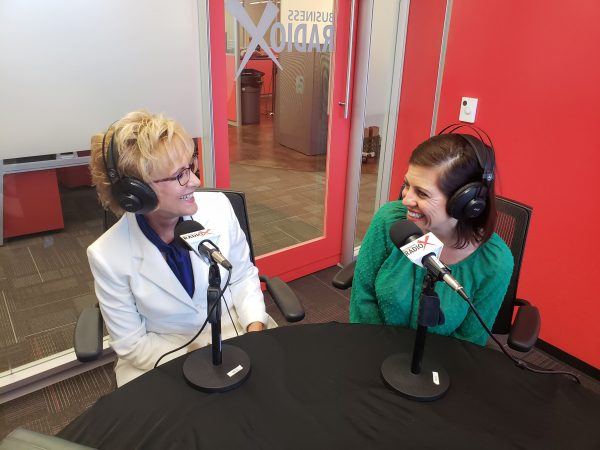
 Gina Ore has enjoyed more than 25 years of successful fundraising and relationship engagement. She has worked with medical professionals, generous donors, and dedicated volunteers who have supported healthcare, medical research, and human services.
Gina Ore has enjoyed more than 25 years of successful fundraising and relationship engagement. She has worked with medical professionals, generous donors, and dedicated volunteers who have supported healthcare, medical research, and human services.













 on engaging authentic and energized employees. Unlike traditional and large consulting companies and individuals, we bring a non-traditional, culturally fresh perspective and learning approach that creates better attachment, demands action and drives results. Our diverse set of experts provide workshops, speeches, strategy development, leadership events, and deep strategy-to-action consulting engagements across the following areas of expertise:
on engaging authentic and energized employees. Unlike traditional and large consulting companies and individuals, we bring a non-traditional, culturally fresh perspective and learning approach that creates better attachment, demands action and drives results. Our diverse set of experts provide workshops, speeches, strategy development, leadership events, and deep strategy-to-action consulting engagements across the following areas of expertise:
 Jen Coyne, Co-Founder & CEO, The PEAK Fleet has long had an entrepreneurial and creative energy, including a love for creating and selling fused glass art. In the corporate world, she has applied that spirit to leading change for 25 years. Helping people thrive is her passion and her reason for creating The PEAK Fleet with co-founder Brian Stinson. She has combined her background as a Certified Public Accountant and Project Management Professional with extensive background in strategy development to develop a strong understanding of business priorities and the ability to translate strategies into action.
Jen Coyne, Co-Founder & CEO, The PEAK Fleet has long had an entrepreneurial and creative energy, including a love for creating and selling fused glass art. In the corporate world, she has applied that spirit to leading change for 25 years. Helping people thrive is her passion and her reason for creating The PEAK Fleet with co-founder Brian Stinson. She has combined her background as a Certified Public Accountant and Project Management Professional with extensive background in strategy development to develop a strong understanding of business priorities and the ability to translate strategies into action. Brian Stinson, Co-Founder, The PEAK Fleet is a father, engineer, and athlete with more than 20 years building high performing teams and driving culture change. Early on, at the University of Washington, Brian discovered Industrial Engineering and realized that “People Engineering” was in his DNA. During his 21 years at Intel Corporation, he learned to combine the science of data and analytics with the power of empathy and authentic relationships to solve real world business problems. Brian developed and led effective and engaged teams across multiple organizations.
Brian Stinson, Co-Founder, The PEAK Fleet is a father, engineer, and athlete with more than 20 years building high performing teams and driving culture change. Early on, at the University of Washington, Brian discovered Industrial Engineering and realized that “People Engineering” was in his DNA. During his 21 years at Intel Corporation, he learned to combine the science of data and analytics with the power of empathy and authentic relationships to solve real world business problems. Brian developed and led effective and engaged teams across multiple organizations.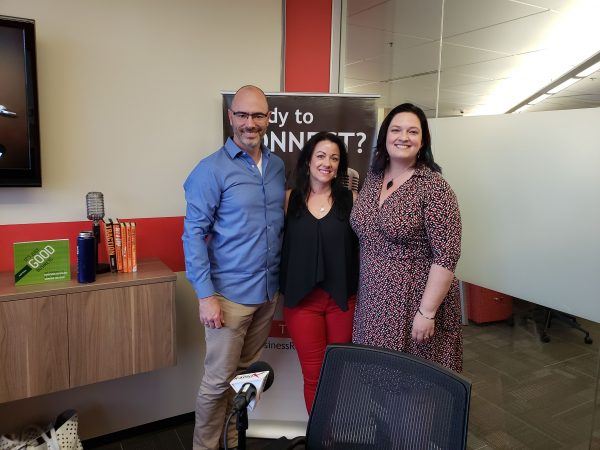 
 Deb Caron is the owner and principal consultant of
Deb Caron is the owner and principal consultant of 


 10am. They will be conducting catered facility tours all day until 8pm and have a car show in our parking lot. This family friendly community event will be a great introduction of their amazing hospital.
10am. They will be conducting catered facility tours all day until 8pm and have a car show in our parking lot. This family friendly community event will be a great introduction of their amazing hospital. Gwen Fulop is an international business executive with 27 years of experience in Arizona. She has spent the last 15 years helping corporations and nonprofit organizations brand themselves in unique ways and grow their business. She now has the blessing of helping Phoenix ER & Medical Hospital do the same.She has brought her entrepreneurial passion and expert medical experience to help brand Arizona’s premier micro-hospital as the best choice for all healthcare needs. She thrives to exceed expectations set by The Valley of The Sun medical community, future patients, and current staff.
Gwen Fulop is an international business executive with 27 years of experience in Arizona. She has spent the last 15 years helping corporations and nonprofit organizations brand themselves in unique ways and grow their business. She now has the blessing of helping Phoenix ER & Medical Hospital do the same.She has brought her entrepreneurial passion and expert medical experience to help brand Arizona’s premier micro-hospital as the best choice for all healthcare needs. She thrives to exceed expectations set by The Valley of The Sun medical community, future patients, and current staff.
 Gina Ore has enjoyed more than 25 years of successful fundraising and relationship engagement. She has worked with medical professionals, generous donors, and dedicated volunteers who have supported healthcare, medical research, and human services. She has also worked in the largest physician-owned practice
Gina Ore has enjoyed more than 25 years of successful fundraising and relationship engagement. She has worked with medical professionals, generous donors, and dedicated volunteers who have supported healthcare, medical research, and human services. She has also worked in the largest physician-owned practice














